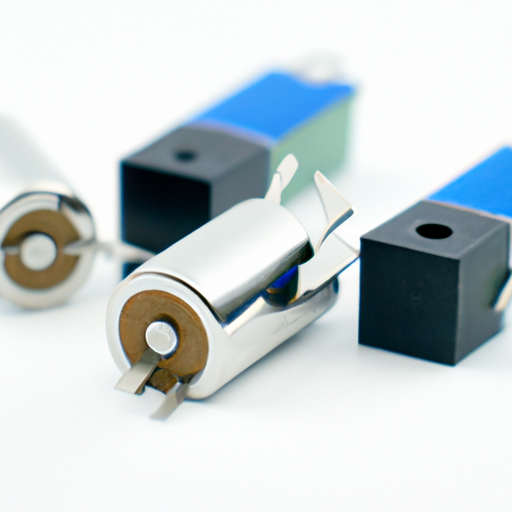
08
17
0
08
16
0
08
15
1
08
14
1
08
13
2