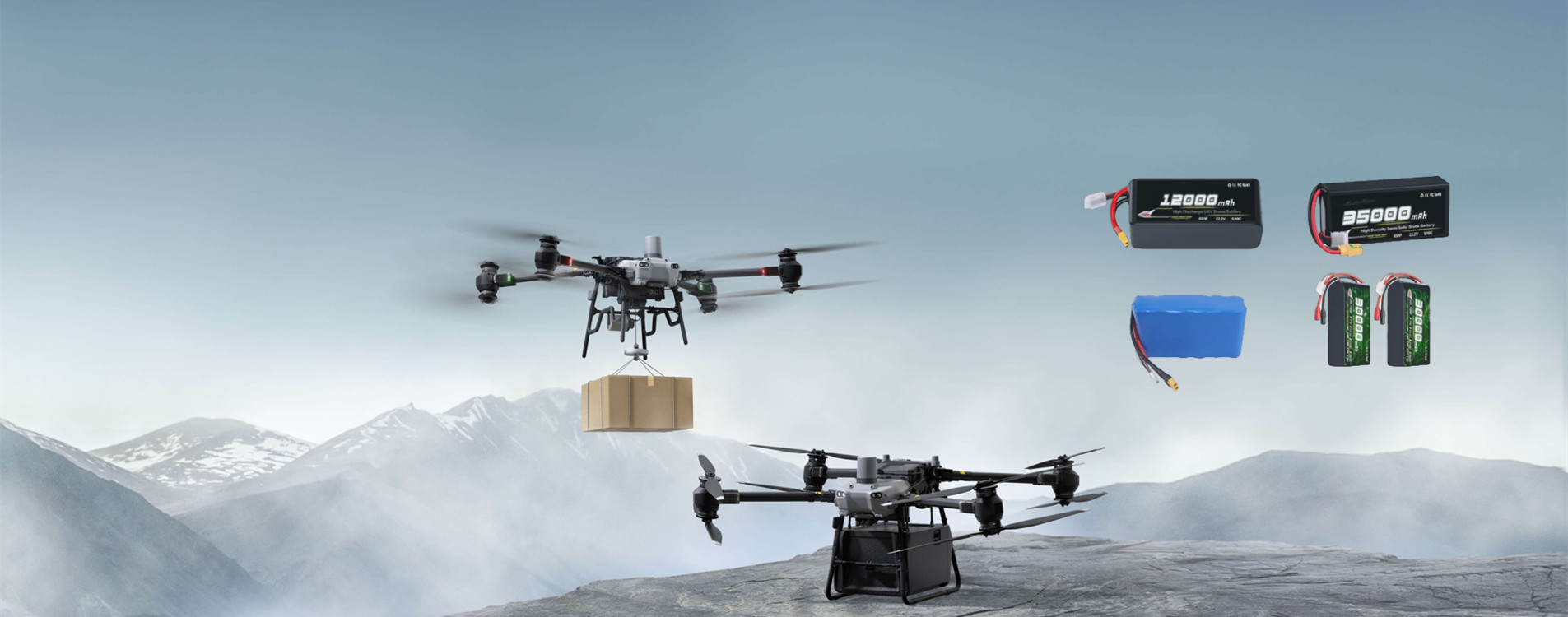
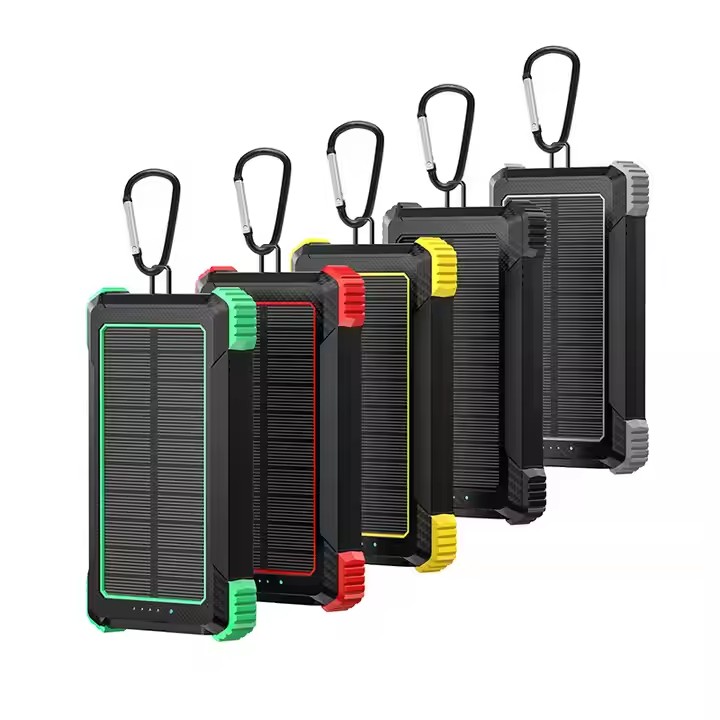
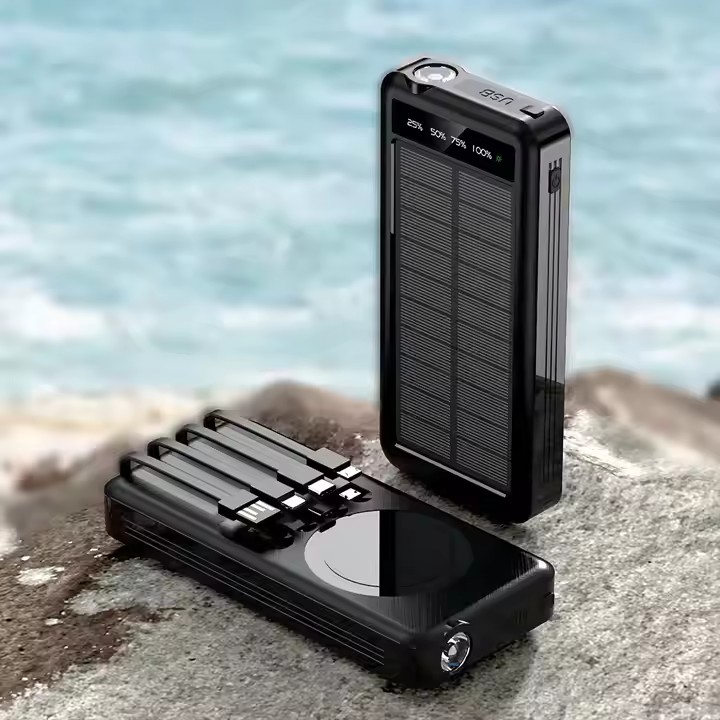
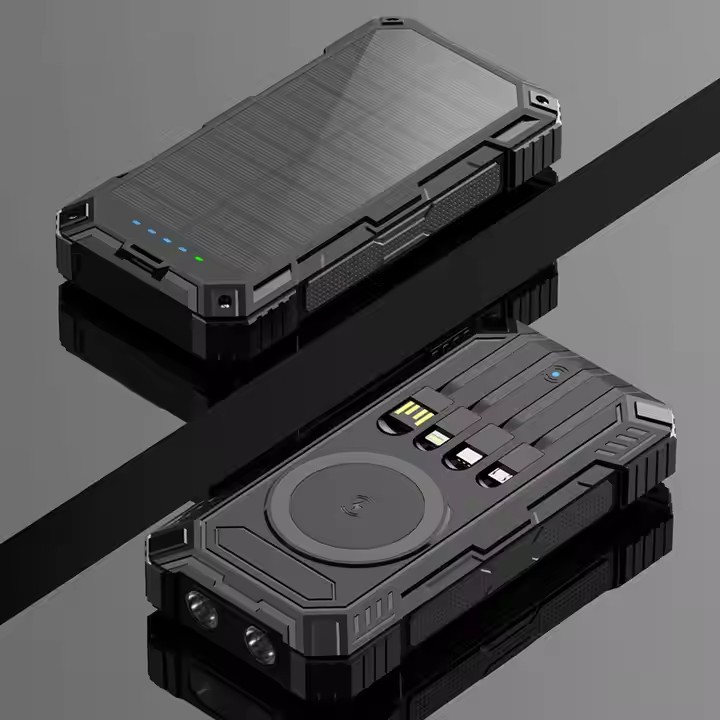
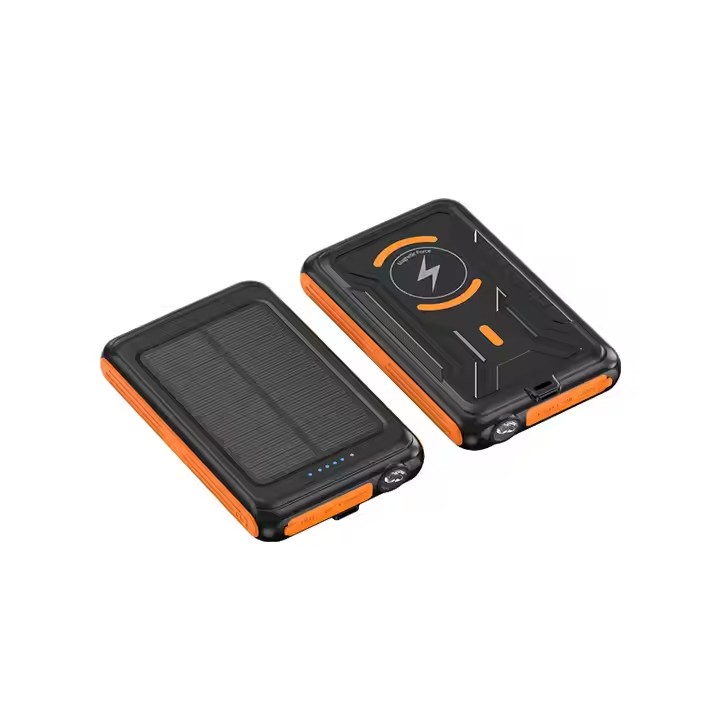
Information
dict2_description
Popular models of common 12v battery chargers
2024-12-18
0
How does a lead-acid battery charger work?
2024-12-17
2
What are the product standards for battery chargers?
2024-12-16
3
dict3_title
dict3_description